Published 2022-08-09.
Time to read: about 6 minutes.
What is Hard Water?
If you find that you need to use a soap in order to get lather that quickly disappears, a white film quickly builds up on your bathroom surfaces and you get white deposits on laundry, you probably have hard water.
Water is called “hard” when it contains a lot of ions from dissolved elements. The most commonly found ions in hard water are from the elements magnesium and calcium. Calcium ions are much more common than magnesium ions in municipal water supplies. 85% of US households have hard water.
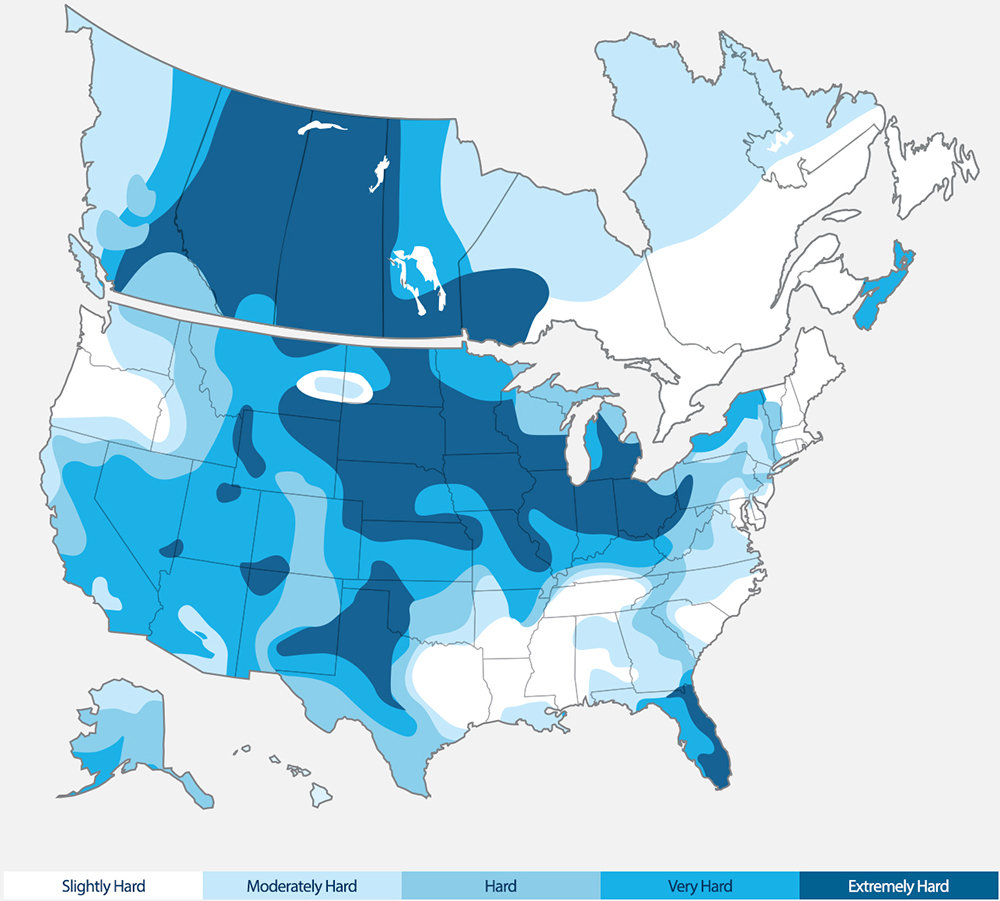
Hardness is measured in parts per million (ppm), which can also be expressed as milligrams per liter (mg/L). The colors in the above map correspond to the following value ranges:
- 0 to 60 mg/L: soft water
- 61 to 120 mg/L: moderately hard water
- 121 to 180 mg/L: hard water
- 181 to 240 mg/L: very hard water
- more than 241 mg/L: extremely hard water
San Antonio, Austin and neighboring areas have some of the hardest water in North America, up to 500 mg/L.
The above map is approximate.
How hard is your water? If you do not have a water softener, and you do not get your water from a well, you can probably find out how hard your water is by visiting your local water authority's website. Here are the water readings for the 10 largest cities in Canada and the US.
| City | Hardness (mg/L) | pH (7.0 is neutral) |
|---|---|---|
| New York City | 65 (moderately hard) | 7.4 |
| Los Angeles | 121 - 142 (hard) | 7.7 |
| Toronto | 111 (moderately hard) | 7 - 8.3 |
| Chicago | 124 - 144 (hard) | 7.8 - 8.2 |
| Houston | 123 (hard) | 7.9 |
| Montreal | 117 (moderately hard) | 7.5 |
| Philadelphia | 100 to 150 (moderately hard to hard) | 7.4 |
| Phoenix | 170 - 284 (hard to very hard) | 7.2 - 8.5 |
| San Antonio | 305 (very hard) | 7.0 |
| San Diego | 174-194 (hard to very hard) | 8.03 |
Hard Water Can Nourish You
Your body needs calcium for bones and teeth. Calcium is the fifth most common element in your body, accounting for approximately 1.5% of the mass of a normal-weight person. The US National Library of Medicine has more information about the human body's need for calcium.
Your body also needs magnesium, and it is the 11th most common element in your body, accounting for 0.1% of the mass of a normal-weight person. According to the US National Library of Medicine, magnesium helps maintain normal nerve and muscle function, maintain a healthy immune system, and keep the heartbeat steady. Magnesium also helps keep bones strong, stablizes blood glucose levels and aids in the production of energy and protein.
Natural hot springs contain the ions of many minerals, and have hard to extremely hard water. Ancient Warmth Bath Salts improves upon nature in this regard.
Hard Water Can Hurt Your House
Hard water slowly deposits on the inside of plumbing pipes, layers itself onto heating elements in hot water tanks. Hard water can also make your hair dry and frizzy, and cause hair color to fade because of the excess mineral buildup. Hard water can make your skin feel not right depending on various factors. So while hard water can be good for for your insides, it is not so good for most things outside.
Protect Your Skin From Unwanted Hard Water
Epsom salts is actually a chemical called magnesium sulfate; it makes water hard when it dissolves because magnesium ions are released into the water. Your body would like to absorb the magnesium but unfortunately the dissolved magnesium sulfate is not absorbed very well by your body. That means you need a lot of Epsom salt to get the magnesium you need, which makes the water even harder than it would ordinarily be.
Skin dries out when exposed to hard water. If you have oily skin that might be a good thing, depending on how hard the water is and therefore how dry your skin gets. Not so nice: fingernails and toenails crack and break more easily, and hair gets brittle and falls out more readily when exposed to hard water. You should control the hardness of your water for the sake of your skin, hair and nails.
If you have hard water, Ancient Warmth Water Softener should be used before adding Ancient Warmth Bath Salts. All bath salts make water hard to some degree, and not all bath salts make water hard the same way or to the same degree. Ancient Warmth Mospe (Epsom spelled backwards) Bath Salts provides a form of magnesioum salt that is more readily absorbed by your skin than Espom salts, so less bath salts are needed, and the water need not be nearly as hard in order to gain the health benefits you desire for the insides of your body. Use Ancient Warmth Mospe – your hair, skin and nails will thank you, along with your muscles, bones, joints, nerves and intestines.
Ancient Warmth Water Softener
Centralized water softeners can be effective if they are properly maintained. For people who do not have such a water softener installed, and who live in an area with hard water, Ancient Warmth offers a non-toxic and environmentally friendly water softener, as a package of powder that can be poured into a bath. Each package contains enough for to soften one full normal-sized (40 US gallons) bathtub by one degree.
Add the number of Ancient Warmth Water Softener packages you need, according to your water's hardness:
- 0 - 60 mg/L: do not worry about hard water
- 61 - 120 mg/L: use 1 package
- 121 - 180 mg/L: use 2 packages
- 181 - 240 mg/L: use 3 packages
- 241 - 300 mg/L: use 4 packages
- 301 - 360 mg/L: use 5 packages
- 361 - 420 mg/L: use 6 packages
- 421 - 480 mg/L: use 7 packages
Incompatible: Bubble Bath and Bath Salts
You could enjoy a bubble bath, or you could enjoy bath salts, but you enjoy both at the same time. Because hard water prevents soap from foaming, and bath salts increases water hardness, any attempt to just add more soap to get foam is doomed. If you see a product that says "Foaming Bath with Pure Epsom Salt" do not buy it… no such product can deliver results as advertised.